



This post discusses a simple example of a Python script which creates a GUI to manipulate an XML document. I have published this post as I could not find many complete examples of this functionality elsewhere on the web.
The example is deliberately simplified to emphasise the code required to read from the XML document, create a GUI window in which the data can be edited and finally to write the changes back to the XML document.
The following image shows the window created by the example:
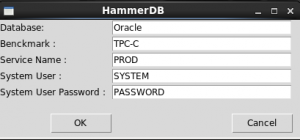
The example is based on the first part of the build options menu of HammerDB. I used HammerDB because it is open source and is written in TCL which uses the same underlying GUI library.
The example was developed on a VM running Python 2.6 and Tkinter 8.5 on Linux 5U4.
I have used the XML Minidom library to manipulate the XML document.
The example XML configuration file (config.xml) is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<hammerdb>
<rdbms>Oracle</rdbms>
<bm>TPC-C</bm>
<oracle>
<service>
<system_user>SYSTEM</system_user>
<system_password>PASSWORD</system_password>
<service_name>PROD</service_name>
</service>
</oracle>
</hammerdb>
To reduce the length of the example, I have only used the first handful of elements in the HammerDB configuration file.
The complete example follows. The remainder of this post discusses the example in detail:
#!/usr/bin/python
import xml.dom.minidom
from ttk import Frame, Label,Entry,Button
from Tkinter import Tk, StringVar, BOTH, W, E
import tkMessageBox
import sys
def printf (format, *args):
sys.stdout.write (format % args)
def fprintf (fp, format, *args):
fp.write (format % args)
# get an XML element with specified name
def getElement (parent,name):
nodeList = []
if parent.childNodes:
for node in parent.childNodes:
if node.nodeType == node.ELEMENT_NODE:
if node.tagName == name:
nodeList.append (node)
return nodeList[0]
# get value of an XML element with specified name
def getElementValue (parent,name):
if parent.childNodes:
for node in parent.childNodes:
if node.nodeType == node.ELEMENT_NODE:
if node.tagName == name:
if node.hasChildNodes:
child = node.firstChild
return child.nodeValue
return None
# set value of an XML element with specified name
def setElementValue (parent,name,value):
if parent.childNodes:
for node in parent.childNodes:
if node.nodeType == node.ELEMENT_NODE:
if node.tagName == name:
if node.hasChildNodes:
child = node.firstChild
child.nodeValue = value
return None
class Application (Frame):
def __init__(self, parent):
# initialize frame
Frame.__init__(self,parent)
# set root as parent
self.parent = parent
# read and parse XML document
DOMTree = xml.dom.minidom.parse ("config.xml")
# create attribute for XML document
self.xmlDocument = DOMTree.documentElement
# get value of "rdbms" element
self.database = StringVar()
self.database.set (getElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"rdbms"))
# get value of "benckmark" element
self.benchmark = StringVar()
self.benchmark.set (getElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"bm"))
# create attribute for "oracle" element
self.xmlOracle = getElement (self.xmlDocument,"oracle")
# create attribute for "service" element
self.xmlService = getElement (self.xmlOracle,"service")
# get value of "system_user" element
self.systemUser = StringVar()
self.systemUser.set (getElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_user"))
# get value of "system_password" element
self.systemPassword = StringVar()
self.systemPassword.set (getElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_password"))
# get value of "service_name" element
self.serviceName = StringVar()
self.serviceName.set (getElementValue (self.xmlService,"service_name"))
# initialize UI
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
# set frame title
self.parent.title ("HammerDB")
# pack frame
self.pack (fill=BOTH, expand=1)
# configure grid columns
self.columnconfigure (0, pad=3)
self.columnconfigure (1, pad=3)
# configure grid rows
self.rowconfigure (0, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (1, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (2, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (3, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (4, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (6, pad=3)
# database
label1 = Label (self,text = "Database: ")
label1.grid (row=0,column=0,sticky=W)
entry1 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.database)
entry1.grid (row=0,column=1)
# bench mark
label2 = Label (self,text = "Benckmark : ")
label2.grid (row=1,column=0,sticky=W)
entry2 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.benchmark)
entry2.grid (row=1,column=1)
# service name
label3 = Label (self,text = "Service Name : ")
label3.grid (row=2,column=0,sticky=W)
entry3 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.serviceName)
entry3.grid (row=2,column=1)
# system user
label4 = Label (self,text = "System User : ")
label4.grid (row=3,column=0,sticky=W)
entry4 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.systemUser)
entry4.grid (row=3,column=1)
# system user password
label5 = Label (self,text = "System User Password : ")
label5.grid (row=4,column=0,sticky=W)
entry5 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.systemPassword)
entry5.grid (row=4,column=1)
# blank line
label6 = Label (self,text = "")
label6.grid (row=5,column=0,sticky=E+W)
# create OK button
button1 = Button (self, text="OK", command=self.onOK)
button1.grid (row=6,column=0,sticky=E)
# create Cancel button
button2 = Button (self, text="Cancel", command=self.onCancel)
button2.grid (row=6,column=1,sticky=E)
def onOK(self):
# set values in xml document
setElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"rdbms",self.database.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"bm",self.benchmark.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_user",self.systemUser.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_password",self.systemPassword.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlService,"service_name",self.serviceName.get())
# open XML file
f = open ("config.xml","w")
# set xml header
fprintf (f,'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>\n')
# write XML document to XML file
self.xmlDocument.writexml (f)
# close XML file
f.close ()
# show confirmation message
tkMessageBox.showerror ("Message","Configuration updated successfully")
# exit program
self.quit();
def onCancel(self):
# exit program
self.quit();
def main():
# initialize root object
root = Tk()
# set size of frame
root.geometry ("410x160+300+300")
# call object
app = Application (root)
# enter main loop
root.mainloop()
# if this is the main thread then call main() function
if __name__ == '__main__':
main ()
The above code is discussed in the following sections:
There are several XML libraries available in Python including Minidom and ElementTree. In this example I have used Minidom which is shipped as part of the base Python release on Linux.
Within Minidom, I have only used the Node class, not the Element, Attribute etc classes. In particular I have avoided using the Element.getElementsByTagName() method as it appears not to support some XML document schema designs.
import xml.dom.minidom
The next set of declarations are for the GUI elements used by ttk and Tkinter. Tkinter (Tk interface) is based on ttk (Themed tk)
from ttk import Frame, Label,Entry,Button from Tkinter import Tk, StringVar, BOTH, W, E
Alternatively all classes could be imported from Tkinter as follows:
from Tkinter import Tk, Frame, Label,Entry,Button, StringVar, BOTH, W, E
The tkMessageBox is a Python widget that is used to display messages in a popup window. The class is imported separately from Tkinter
import tkMessageBox
The next declarations define equivalents of the C printf and fprintf functions. I normally include these functions in a separate library.
import sys
def printf (format, *args):
sys.stdout.write (format % args)
def fprintf (fp, format, *args):
fp.write (format % args)
The getElement method traverses the list of child nodes for a specfied parent node. If the child is an element and the tag matches a specified name then the node is added to a list. The first element of the node list is returned. Note that this function works with this example as a child node will always be found, but the function is not robust.
# get an XML element with specified name
def getElement (parent,name):
nodeList = []
if parent.childNodes:
for node in parent.childNodes:
if node.nodeType == node.ELEMENT_NODE:
if node.tagName == name:
nodeList.append (node)
return nodeList[0]
The getElementValue method also traverses the list of child nodes for the specified parent node searching for elements with tags that match the specified name. If the element has children then the value of the first child is returned. Again this method makes assumptions about the presence and type of the child and is therefore not robust.
# get value of an XML element with specified name
def getElementValue (parent,name):
if parent.childNodes:
for node in parent.childNodes:
if node.nodeType == node.ELEMENT_NODE:
if node.tagName == name:
if node.hasChildNodes:
child = node.firstChild
return child.nodeValue
return None
The setElementValue method is similar to getElementValue, except that it updates the value of the child node with the value passed as an argument.
# set value of an XML element with specified name
def setElementValue (parent,name,value):
if parent.childNodes:
for node in parent.childNodes:
if node.nodeType == node.ELEMENT_NODE:
if node.tagName == name:
if node.hasChildNodes:
child = node.firstChild
child.nodeValue = value
return None
The Application class contains the application logic including reading, updating and writing the XML document and creating / managing the GUI.
class Application (Frame):
The __init__ method is called when a new instance of the class is created
def __init__(self, parent):
The first step is to initialize the frame
# initialize frame
Frame.__init__(self,parent)
The parent of the class (in this case root) is stored as an attribute for later use
# set root as parent
self.parent = parent
The XML document ("config.xml") is parsed and stored in a DOM tree
# read and parse XML document
DOMTree = xml.dom.minidom.parse ("config.xml")
An attribute is created for the XML document
# create attribute for XML document
self.xmlDocument = DOMTree.documentElement
The variables for the oracle elements - rdbms and benchmark are initialized
# get value of "rdbms" element
self.database = StringVar()
self.database.set (getElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"rdbms"))
# get value of "benchmark" element
self.benchmark = StringVar()
self.benchmark.set (getElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"bm"))
An attribute is created for the "oracle" element
# create attribute for "oracle" element
self.xmlOracle = getElement (self.xmlDocument,"oracle")
An attribute is created for the "service" element
# create attribute for "service" element
self.xmlService = getElement (self.xmlOracle,"service")
In the next section the variables for the service elements - system_user, system_password and service_name are initialised using getElementValue to read them from the xmlService element
# get value of "system_user" element
self.systemUser = StringVar()
self.systemUser.set (getElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_user"))
# get value of "system_password" element
self.systemPassword = StringVar()
self.systemPassword.set (getElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_password"))
# get value of "service_name" element
self.serviceName = StringVar()
self.serviceName.set (getElementValue (self.xmlService,"service_name"))
Finally the UI is initialized by calling the initUI procedure
# initialize UI
self.initUI()
The initUI() method is probably redundant in this example, but is typically used to initialize the user interface
def initUI(self):
The first step sets the title of the applicaation frame
# set frame title
self.parent.title ("HammerDB")
The frame is initialized using the Pack layout manager. If this statement is omitted, the frame will still be drawn, but will appear as an empty grey box.
# pack frame
self.pack (fill=BOTH, expand=1)
The grid layout manager will be used for the rest of the UI initialization.
First the two columns are created:
# configure grid columns
self.columnconfigure (0, pad=3)
self.columnconfigure (1, pad=3)
Next the six columns are created:
# configure grid rows
self.rowconfigure (0, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (1, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (2, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (3, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (4, pad=3)
self.rowconfigure (6, pad=3)
Each variable has a label and and entry
The label is left-justified using the sticky=w parameter
# database
label1 = Label (self,text = "Database: ")
label1.grid (row=0,column=0,sticky=W)
entry1 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.database)
entry1.grid (row=0,column=1)
# bench mark
label2 = Label (self,text = "Benckmark : ")
label2.grid (row=1,column=0,sticky=W)
entry2 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.benchmark)
entry2.grid (row=1,column=1)
# service name
label3 = Label (self,text = "Service Name : ")
label3.grid (row=2,column=0,sticky=W)
entry3 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.serviceName)
entry3.grid (row=2,column=1)
# system user
label4 = Label (self,text = "System User : ")
label4.grid (row=3,column=0,sticky=W)
entry4 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.systemUser)
entry4.grid (row=3,column=1)
# system user password
label5 = Label (self,text = "System User Password : ")
label5.grid (row=4,column=0,sticky=W)
entry5 = Entry (self,width=30,textvariable = self.systemPassword)
entry5.grid (row=4,column=1)
A label is used to insert a blank line to create a space in the grid between the variables and buttons.
# blank line
label6 = Label (self,text = "")
label6.grid (row=5,column=0,sticky=E+W)
An OK button is created which calls the onOk() method when clicked
# create OK button
button1 = Button (self, text="OK", command=self.onOK)
button1.grid (row=6,column=0,sticky=E)
Finally a Cancel button is created which calls the onCancel() method when clicked
# create Cancel button
button2 = Button (self, text="Cancel", command=self.onCancel)
button2.grid (row=6,column=1,sticky=E)
The onOK method is called when the OK button is clicked. It writes the new variable settings back to the XML document.
def onOK(self):
The first step sets the current values of the variables in the XML document
# set values in xml document
setElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"rdbms",self.database.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlDocument,"bm",self.benchmark.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_user",self.systemUser.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlService,"system_password",self.systemPassword.get())
setElementValue (self.xmlService,"service_name",self.serviceName.get())
The XML document is written back to the XML file using the writexml method. There is probably a more elegant way of setting the XML header
# open XML file
f = open ("config.xml","w")
# set xml header
fprintf (f,'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>\n')
# write XML document to XML file
self.xmlDocument.writexml (f)
# close XML file
f.close ()
A confirmation message is shown using the tkMessageBox widget
# show confirmation message
tkMessageBox.showerror ("Message","Configuration updated successfully")
Finally we can quit the application
# exit program
self.quit();
The onCancel method is called when the Cancel button is clicked. It exits the application without saving any changes
def onCancel(self):
# exit program
self.quit();
The main () function is called to initialize the root object, set the size of the frame, create an Application object and then enter the main loop until the application exits
def main():
# initialize root object
root = Tk()
# set size of frame
root.geometry ("410x160+300+300")
# call object
app = Application (root)
# enter main loop
root.mainloop()
If this is the main thread then call the main () function:
if __name__ == '__main__': main ()